
Blood performs many important functions in the body.

The test is useful to detect hyperthyroidism or blood viscosity to decide on a treatment option. Especially valuable for patients with diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, polycythemia vera, arteritis of the lower extremities, and hypergammaglobulinemia. The blood viscosity test is very valuable in the evaluation of thrombotic diseases. However, it is often difficult to determine whether the detected abnormalities are the true cause or effect of clinical thrombotic events. Among these diseases, can include diabetes, high blood pressure or hyperlipidemia. There are many diseases that are often associated with thrombotic complications and are accompanied by increased blood viscosity, increased erythrocyte aggregation or decreased ability to change the shape of red blood cells. In addition, these proteins cause the formation of erythrocytes and predispose to thrombotic complications. Plasma viscosity: increasing high molecular weight protein increases plasma viscosity, thus increasing blood viscosity. This aggregation of red blood cells causes a decrease in blood flow and an increase in blood viscosity. Aggregation of RBCs: Aggregation proteins that are able to bind red blood cells together to form erythrocytes are fibrinogen, globulins, very low-density lipoproteins, and circulating immune complexes. Some pathologies that deform red blood cells, such as sickle cell anemia, are associated with a decreased ability to change the shape of red blood cells with secondary increase in blood viscosity.
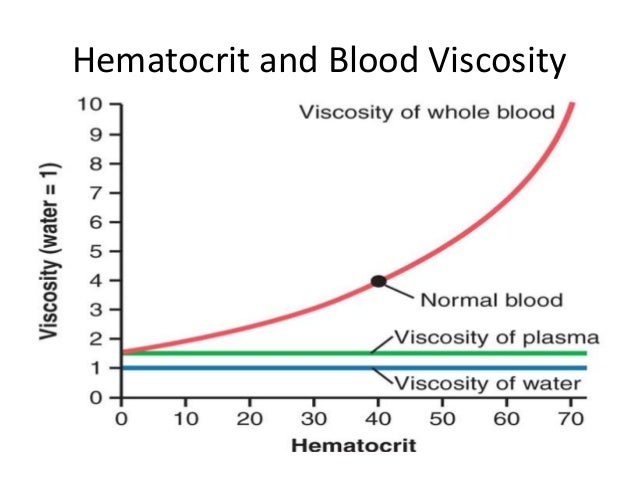
Therefore, red blood cells must change shape to adapt, being able to pass through the peripheral capillaries. Deformability of erythrocytes: mean diameter of capillaries is generally <5 μ, while mean diameter of red blood cells is 7-8 μm. Hemoconcentration: Concentration is often accompanied by increased blood viscosity. In case of loss of a lot of water, not only changes in viscosity, but also is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and imbalanced homeostasis, so it is necessary to add physiological solutions to the body Blood viscosity is sub-par Depending on many different factors such as: Number of cellular components: polycythemia vera or thrombocytosis or a severe increase in white blood cell count can increase blood viscosity. Viscosity increases when the body loses water due to diarrhea, loss of sweat during labor or sudden cold. Normal value of blood viscosity is 2.3 - 4.1 centipoise at 37 degrees Celsius. Viscosity of blood is related to many co-morbid diseases with thrombotic complications.īlood viscosity is determined by red blood cells and plasma protein composition. If blood viscosity increases, it will make blood can not flow freely in arteries, reduce blood flow to organs such as heart, kidneys, brain. The viscosity of blood is 4-6 times that of water, it depends on the number of red blood cells. Physical and chemical properties of blood characterized by density of blood, viscosity, osmotic pressure. Blood maintains osmotic pressure and acid-base balance. Blood protects the body through white blood cells, antibodies and a buffer system, participates in the regulation of body functions and chemical processes thanks to its ability to transmit hormones. Blood plays an important role in the process of respiration, transporting O2 from the lungs to cells and tissues, and bringing CO2 from the cells to the lungs to be eliminated. The main functions of blood are protection, excretion, regulation and nutrition. Blood circulates inside the veins and arteries and performs many important physiological functions. Blood tissue consists of blood cells called red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and extracellular fluid called plasma. Blood is a red liquid tissue, salty taste, formed together with the vascular system, is an important organizational component of the body, the volume of blood is 1/13 of the body weight.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
